- Published on
[AWS] - Load Balancers
- Authors

- David Nguyen
Table of Contents
1. What are we going to do?
Explore some basic knowledge about Elastic Load Balancer (ELB).
Creating a demo Application Load Balancer with two EC2 instances using Target Group.
2. Elastic Load Balancing (ELB).
2.1 - What and why we need load balancing?
- What is Load Balancing?
-> Load balancing is a general term and it helps distribute incoming requests and traffic evenly across multiple servers. The main goal of load balancing is to ensure high availability, reliability, and performance by avoiding overloading a single server and avoiding downtime.
- What is Elastic Load Balancing?
-> Elastic Load Balancing is a type of load balancing developed and managed by AWS. Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes your incoming traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, in one or more Availability Zones. It monitors the health of its registered targets, and routes traffic only to the healthy targets. Elastic Load Balancing scales your load balancer capacity automatically in response to changes in incoming traffic.
- Why should we use ELB?
-> If you want to create and manage your own load balancer, you'll need to prepare for several things, such as servers, technologies, and ensuring it operates correctly, along with other related tasks. While you have full control over access, you'll also need to manage many aspects yourself.
-> ELB is a managed load balancer and AWS guarantees that it will be working, takes care of upgrades, maintenance, high availability, and provides only a few configuration. It costs less to setup your own load balancer.
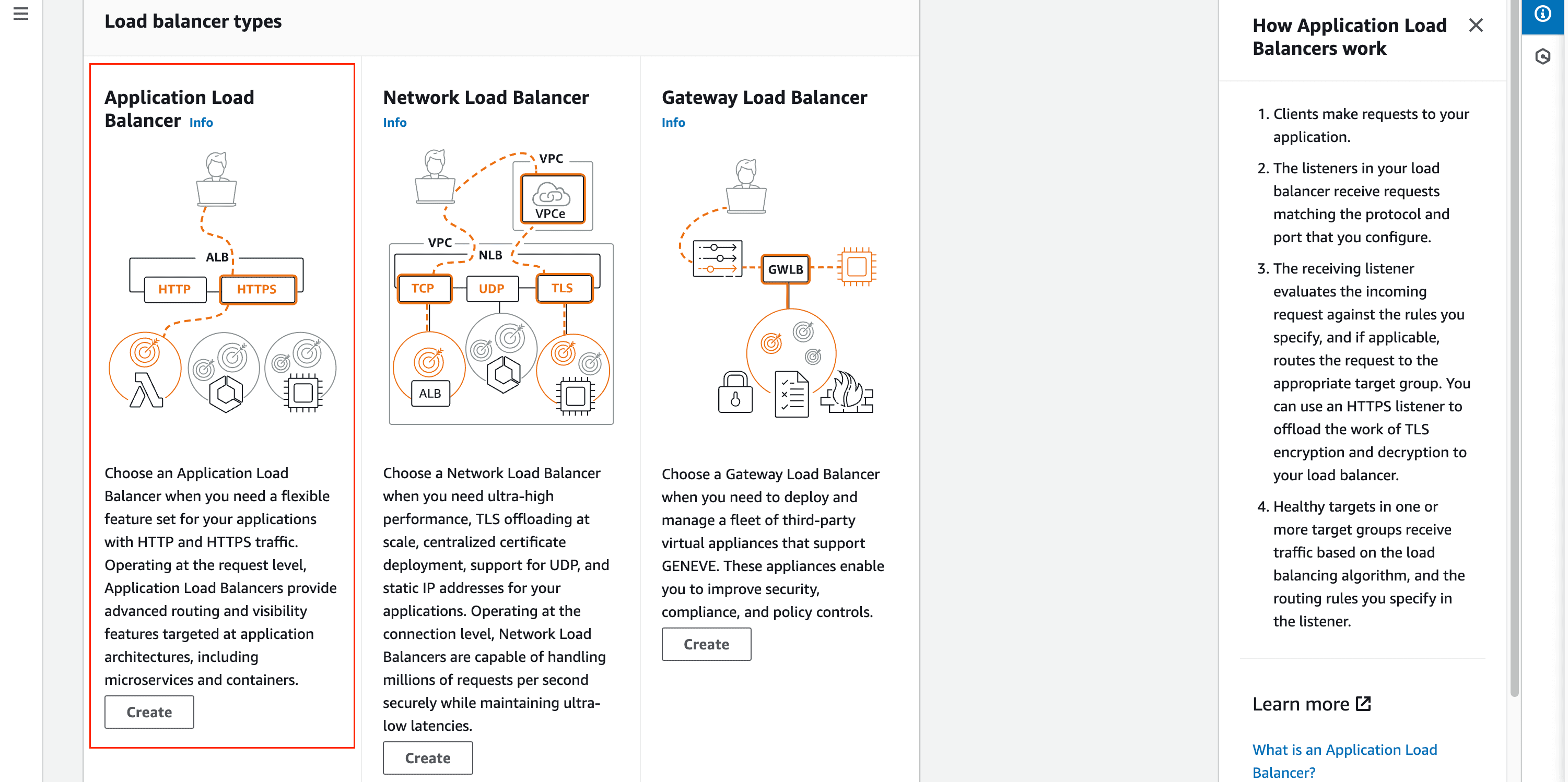
2.2 - Application Load Balancer (ALB).
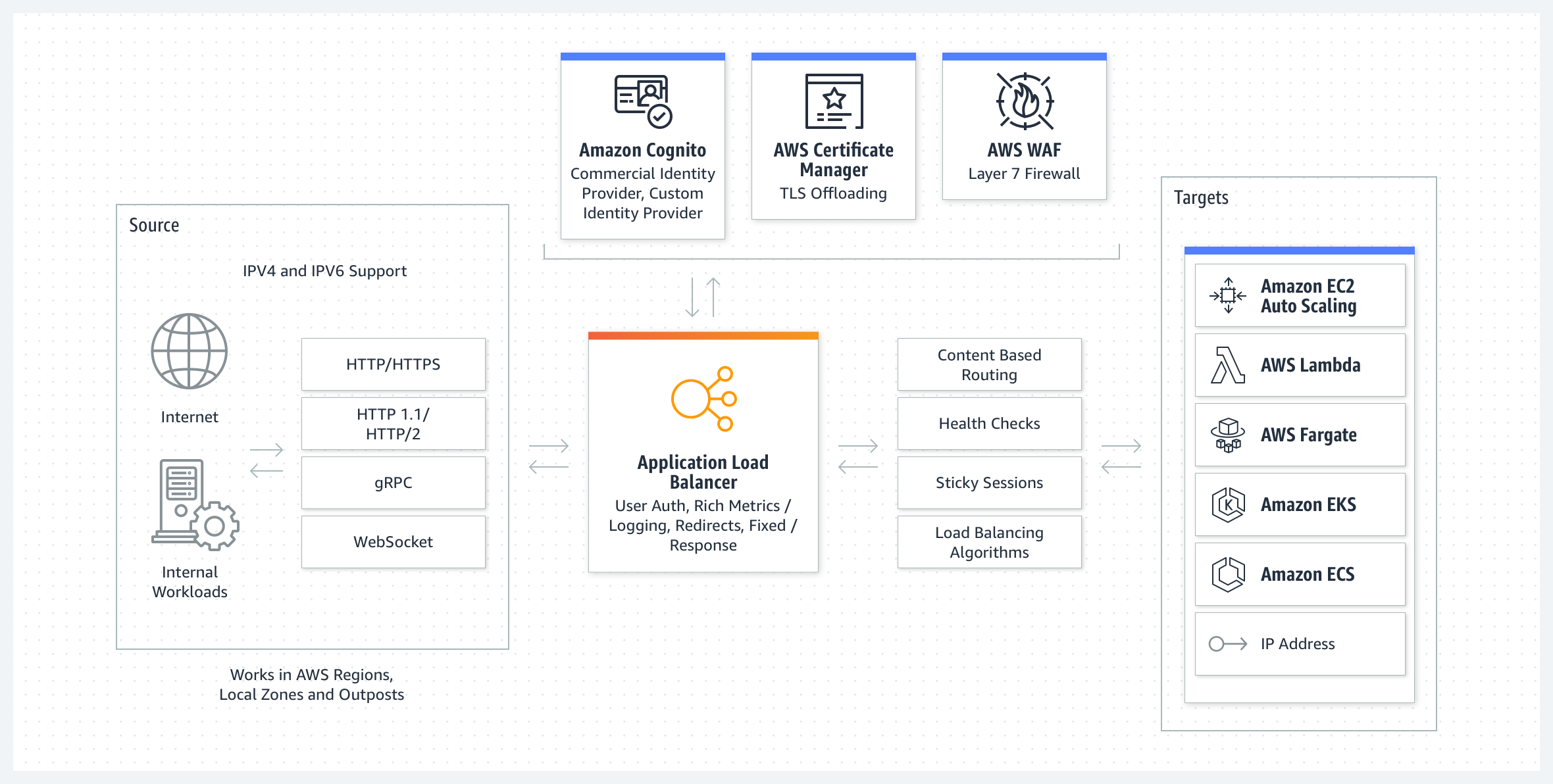
Application Load Balancer flow
-> What is Application Load Balancer?
It's a service that operates at the application layer (layer 7 of the OSI model), designed to distribute incoming HTTP/HTTPS traffic to multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses.
-> Key features?
- Content-based Routing
- Target Groups
- Health Checks
- Autoscaling Integration
- SSL Termination
-> How it works?
- Clients make requests to your application.
- The listeners in your load balancer receive requests matching the protocol and port that you configure.
- The receiving listener evaluates the incoming request against the rules you specify, and if applicable, routes the request to the appropriate target group. You can use an HTTPS listener to offload the work of TLS encryption and decryption to your load balancer.
- Healthy targets in one or more target groups receive traffic based on the load balancing algorithm, and the routing rules you specify in the listener.
2.3 - Gateway Load Balancer:
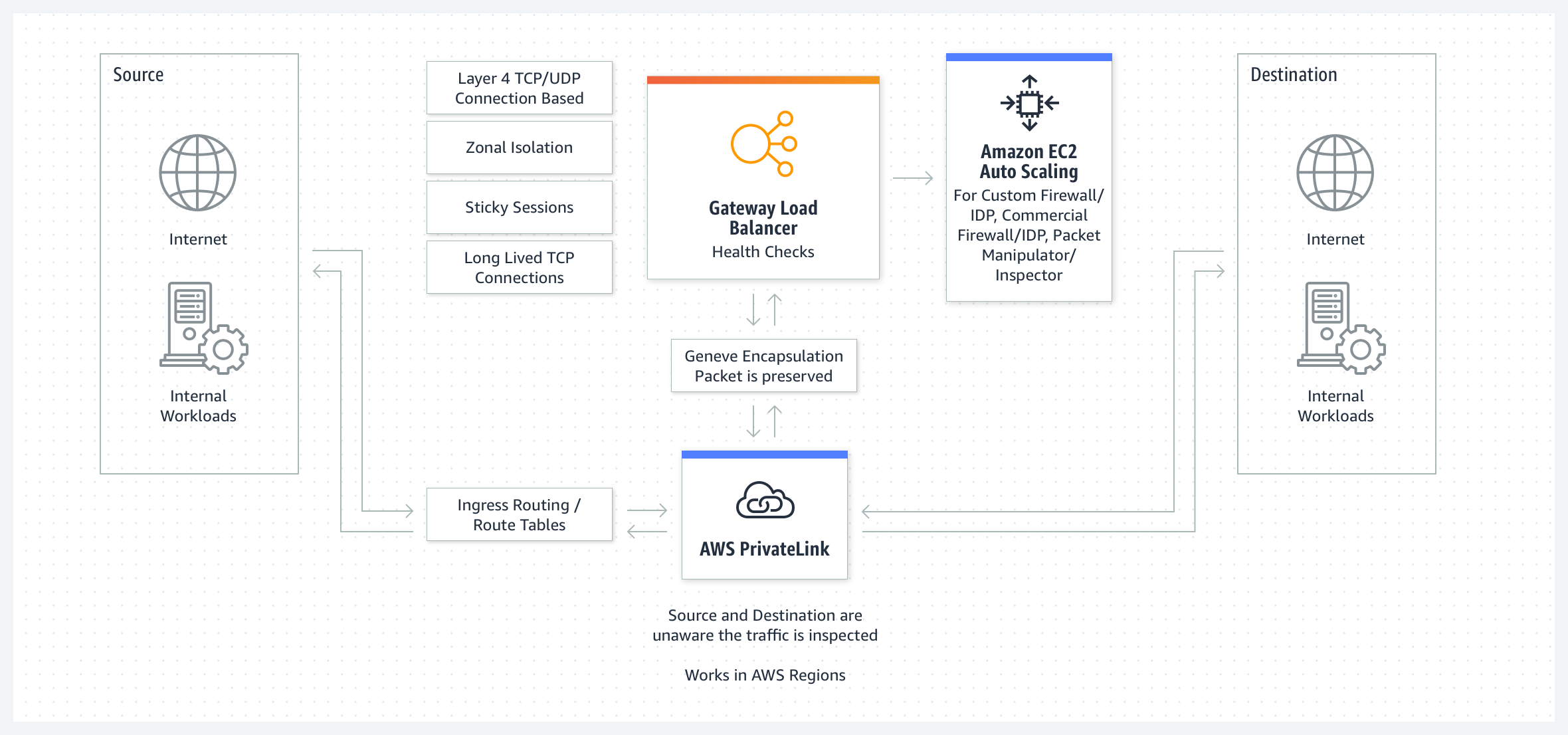
Gateway Load Balancer flow
-> What is Gateway Load Balancer?
It's a service operates at the network layer (layer 3 of the OSI model), designed to handle and distribute network traffic for third-party such as firewalls, prevention systems or network monitoring solutions.
-> Key features:
- Elastic Scaling
- Health Checks
- Appliance Load Balancing
- Integration with AWS services
-> How it works?
- Clients make requests to your application.
- The load balancer receives the request based on the route table configurations that are set within your VPC, Internet Gateway, or Transit Gateway.
- The load balancer routes requests to a target group consisting of a scalable fleet of appliances (for example, firewalls, deep packet inspection systems, URL filtering systems etc.) to process traffic flows.
- The virtual appliance processes the traffic, and forwards it back to the load balancer, or drops the traffic based on its configuration. This type of load balancer acts as a bump-in-the-wire between the source and destination.
- The load balancer forwards the traffic to its destination.
2.4 - Network Load Balancer:
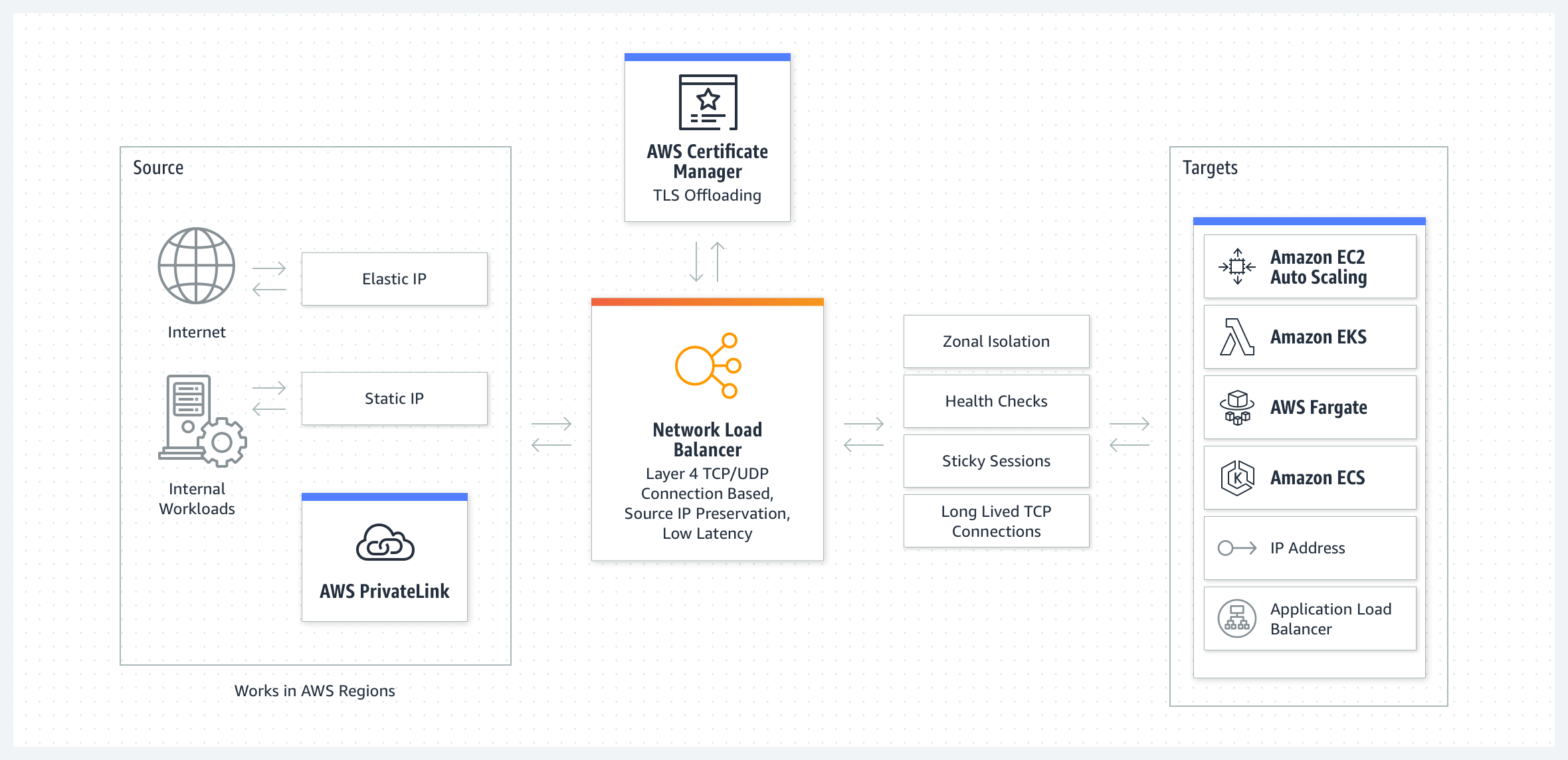
Network Load Balancer flow
-> What is Network Load Balancer?
Network Load Balancer operates at the transport layer (layer 4 of the OSI model), designed to handle high-performance, low-latency traffic and distribute it across multiple EC2 instances, containers, or IP addresses.
-> Key features.
- Static IP
- Health Checks
- Elastic IP support
- Integration with VPC and IP Addressing
-> How it works?
- Clients make requests to your application.
- The load balancer receives the request either directly or through an endpoint for private connectivity (via AWS PrivateLink).
- The listeners in your load balancer receive requests of matching protocol and port, and route these requests based on the default action that you specify. You can use a TLS listener to offload the work of encryption and decryption to your load balancer.
- Healthy targets in one or more target groups receive traffic according to the flow hash algorithm.
-> Next steps, we will walk through an example of manually creating a simple Application Load Balancer with two EC2 instances using Target Group.
4. Hands-on.
Step 1: Create two (or more) EC2 instances:
- Enter instances name and number of instances is 2 (or more if you want).
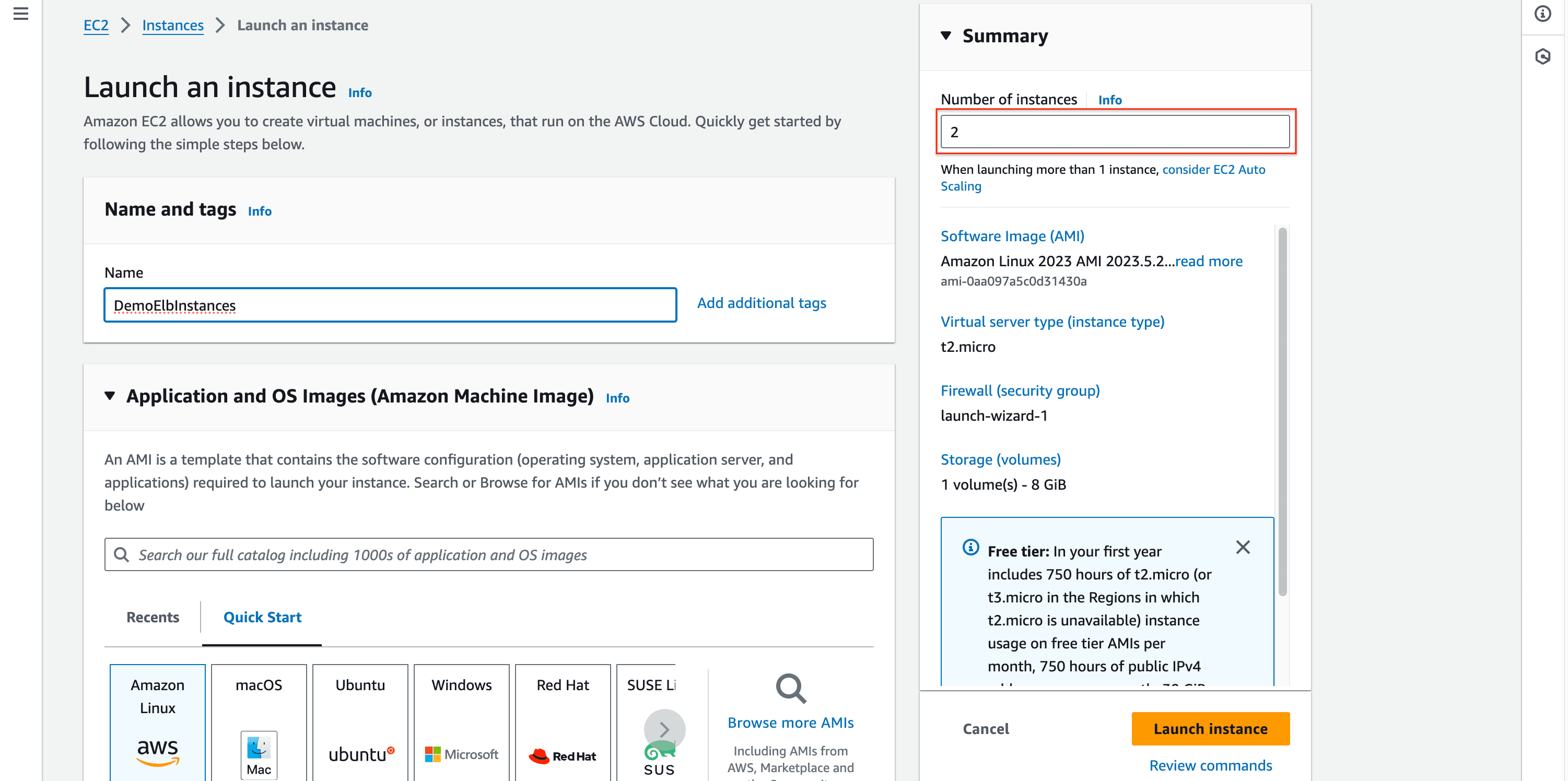
- Choose instances type ->
t2.micro(free tier eligible).
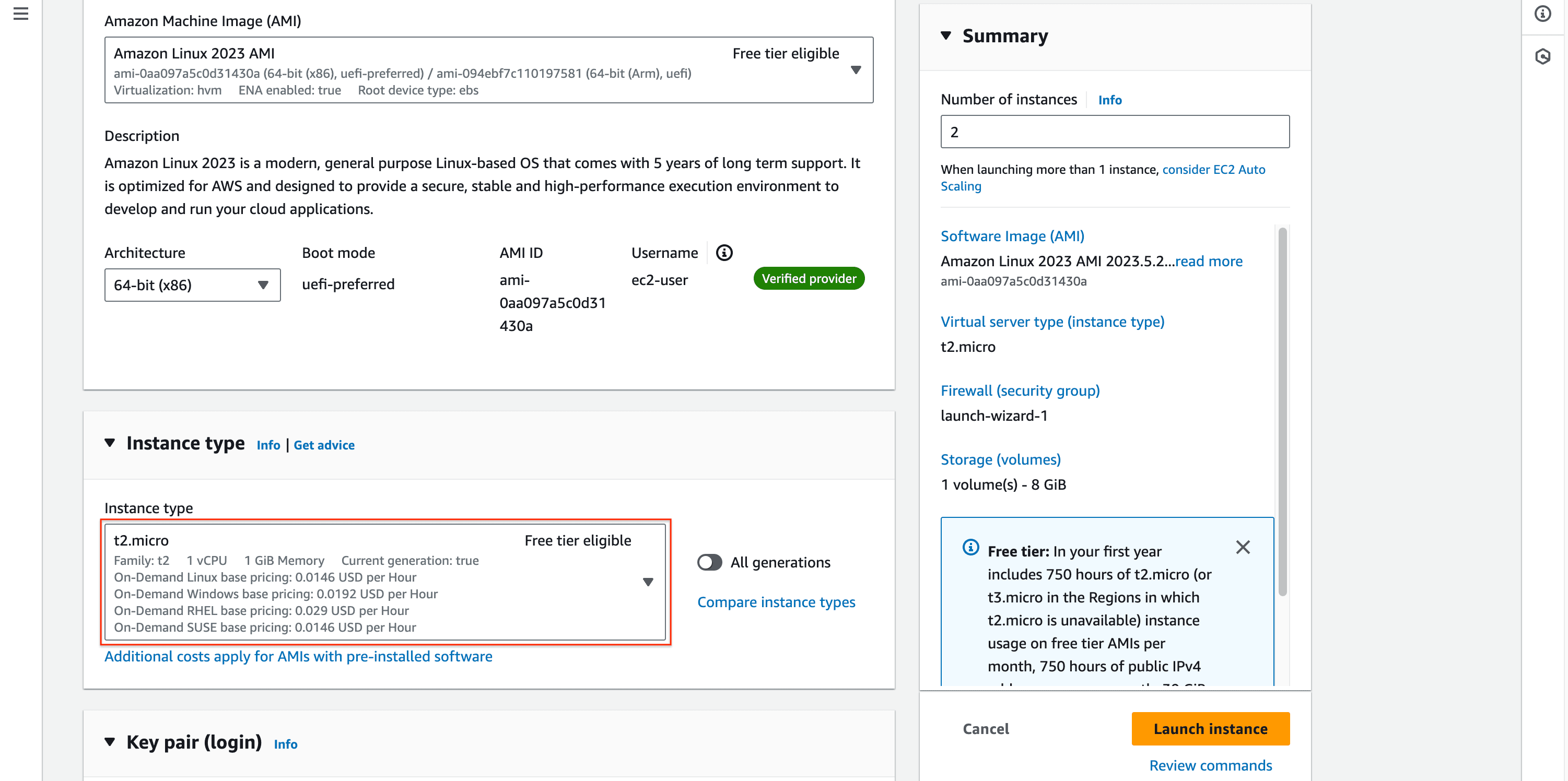
- Generate key pair for securing connect to instances (we will install nginx via SSH later).
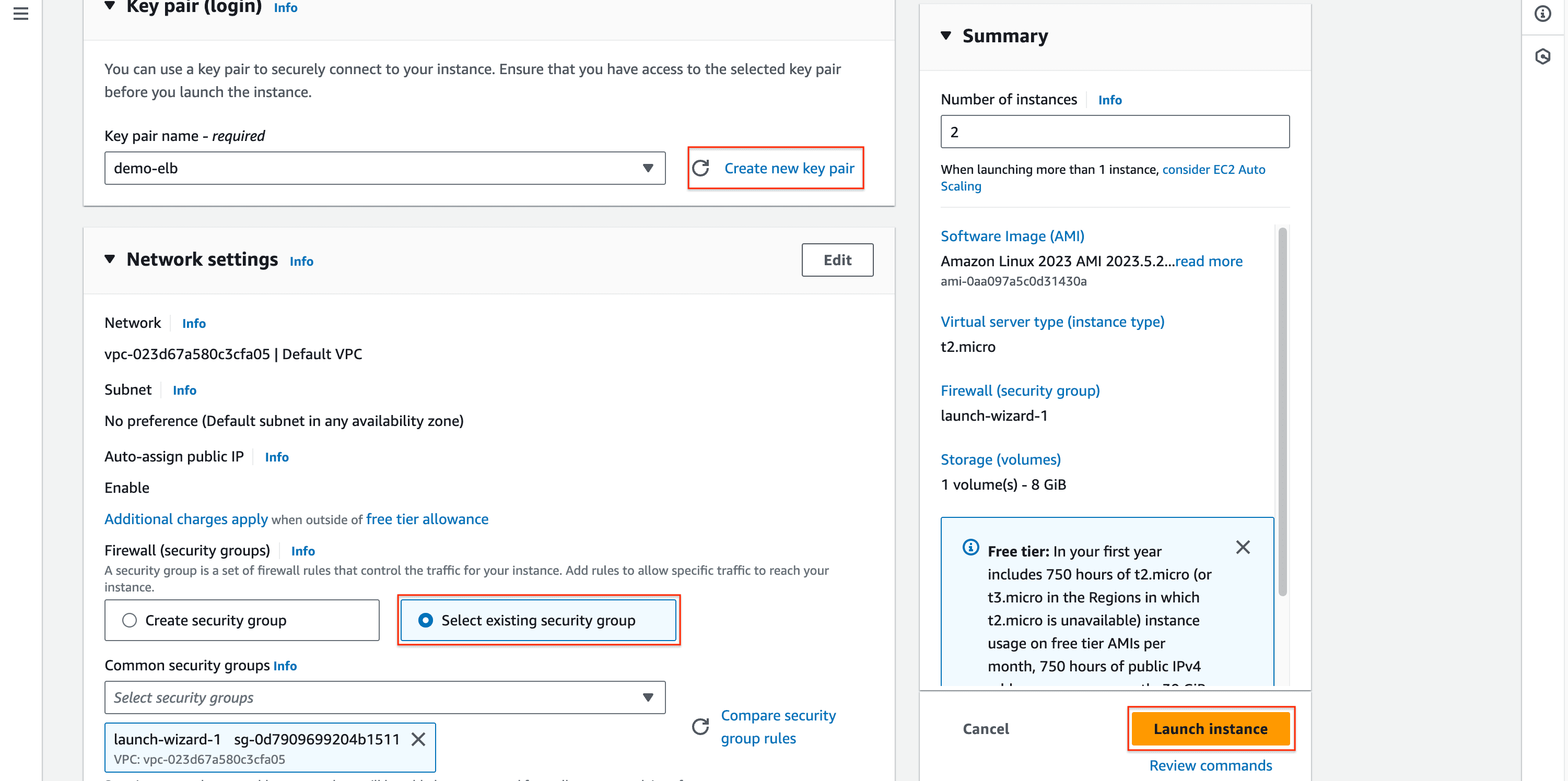
- Edit instances name and we have two EC2 instances are running.
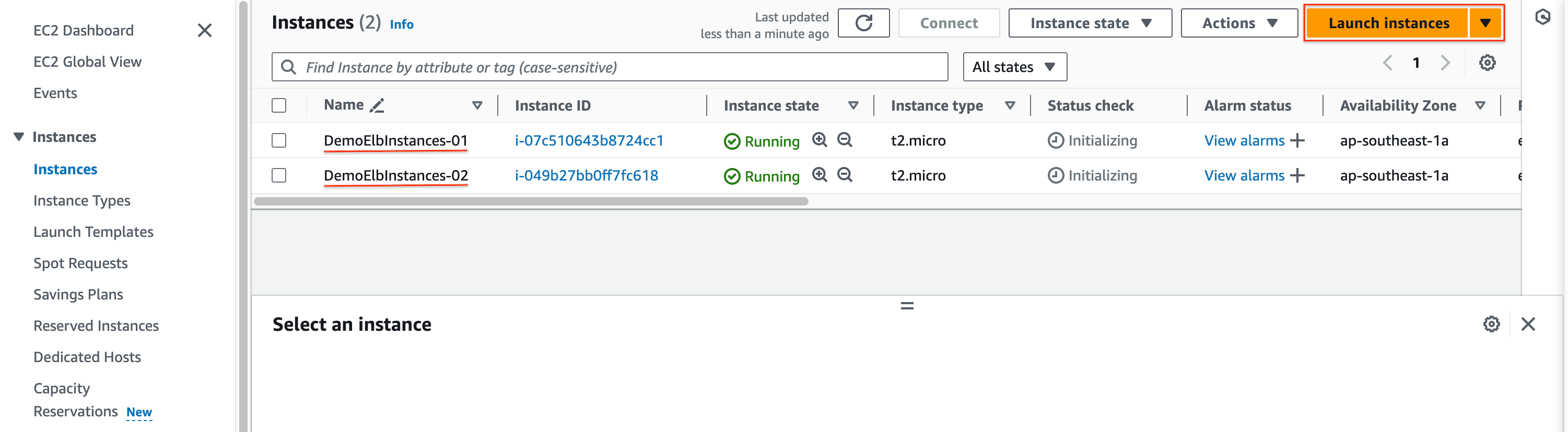
-> To install Nginx for each instance, you can follow my previous post here
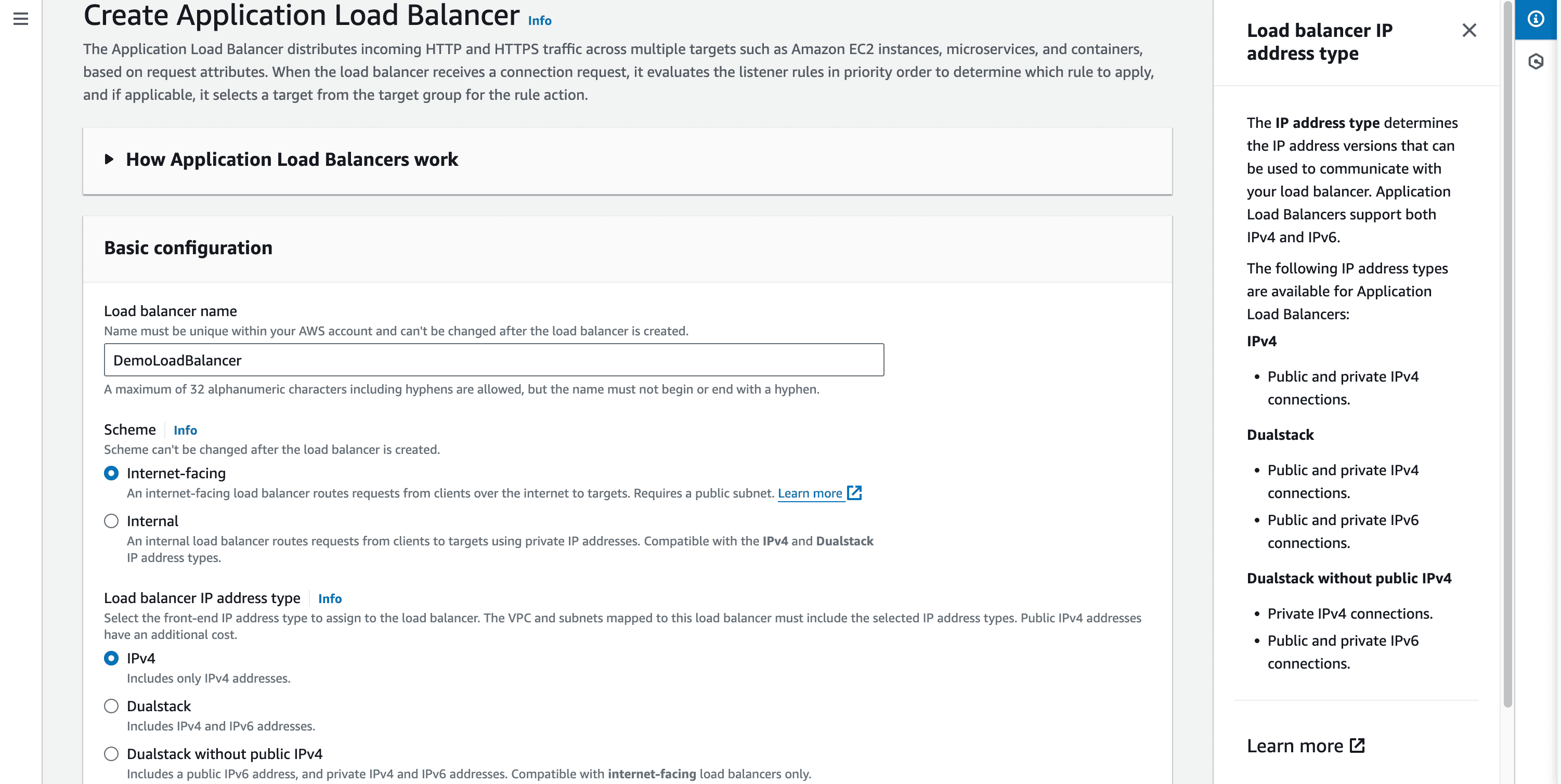
Step 2: Setup Application Load Balancer manually.
-> EC2 -> Load Balancers -> Create load balancer
Choose Application Load Balancer -> Create (You can click on Info to get a brief overview of how the Application Load Balancer works).
- Enter load balancer name and leave basic configuration default.
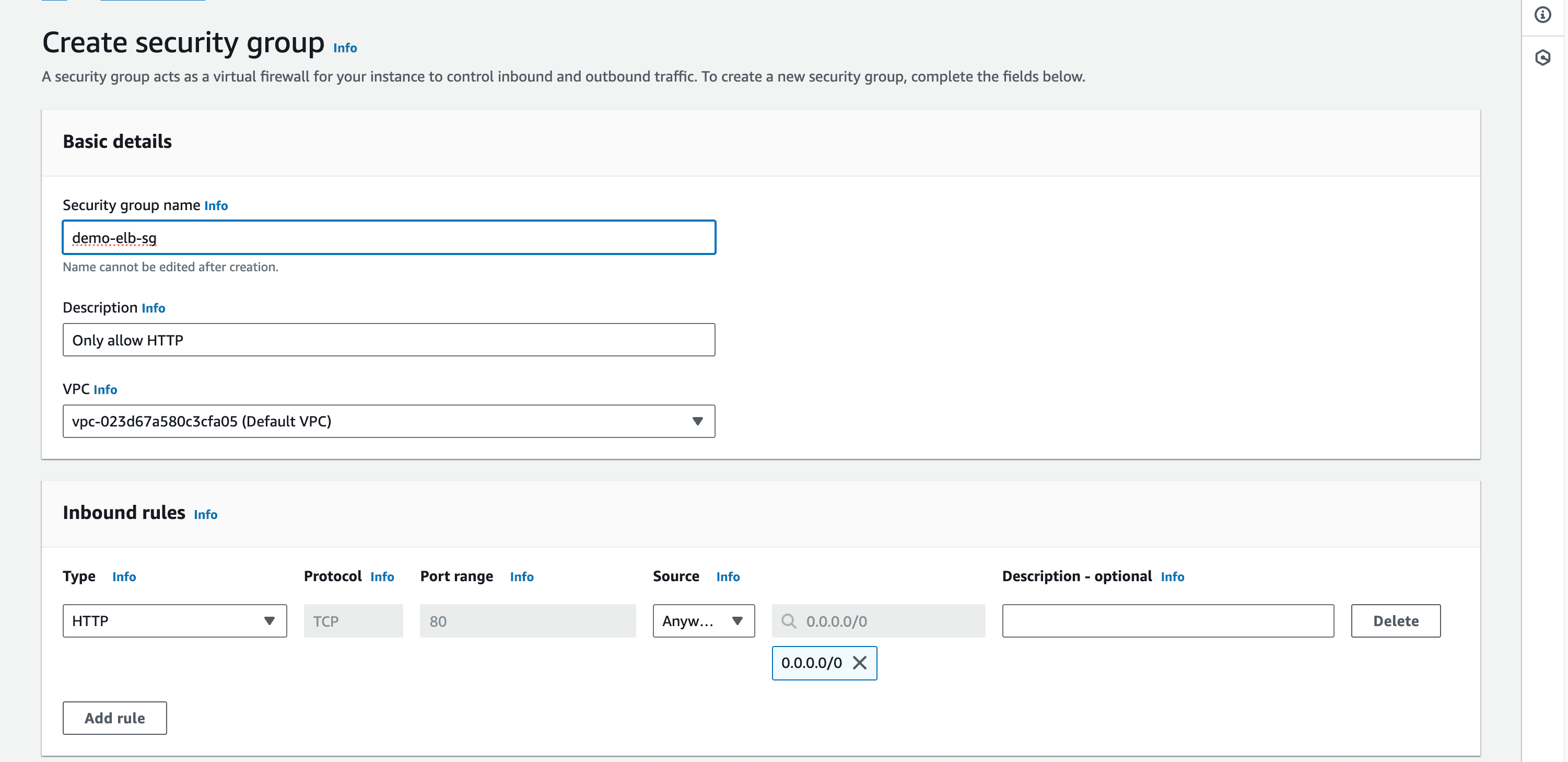
-> Security Group
- Create new Security Group and allow only HTTP requests into ALB.
-> Target Group
- Target group is a logical grouping of instances, containers, or IP addresses that receive the traffic routed by the load balancer. It plays a crucial role in defining how traffic is distributed among the back-end resources.
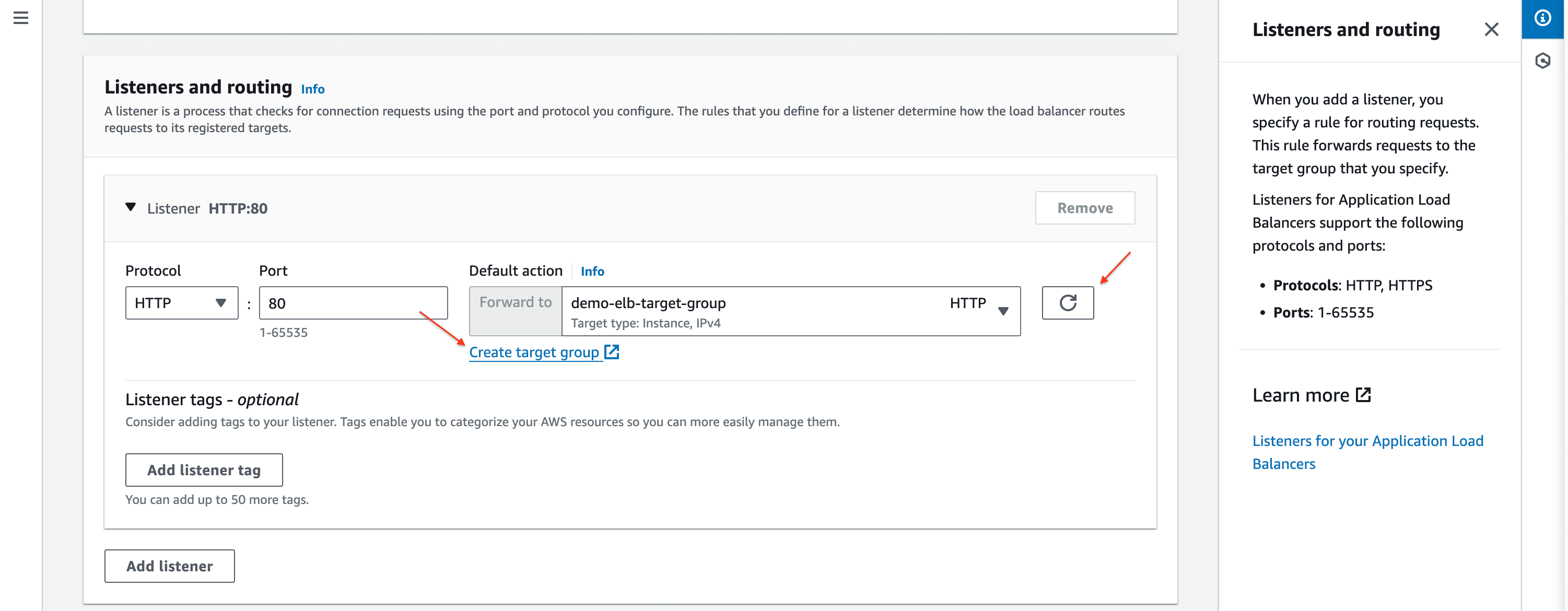
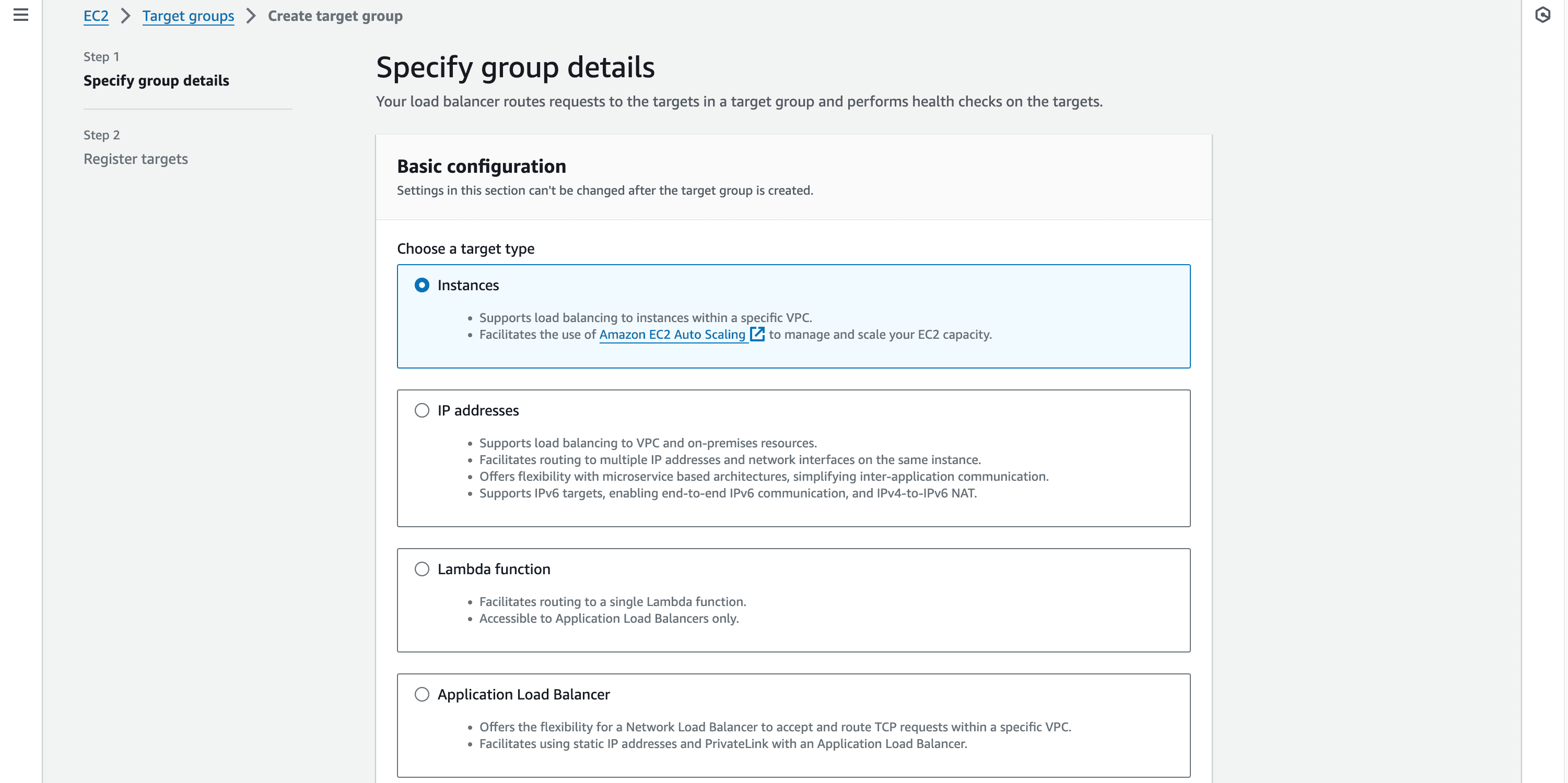
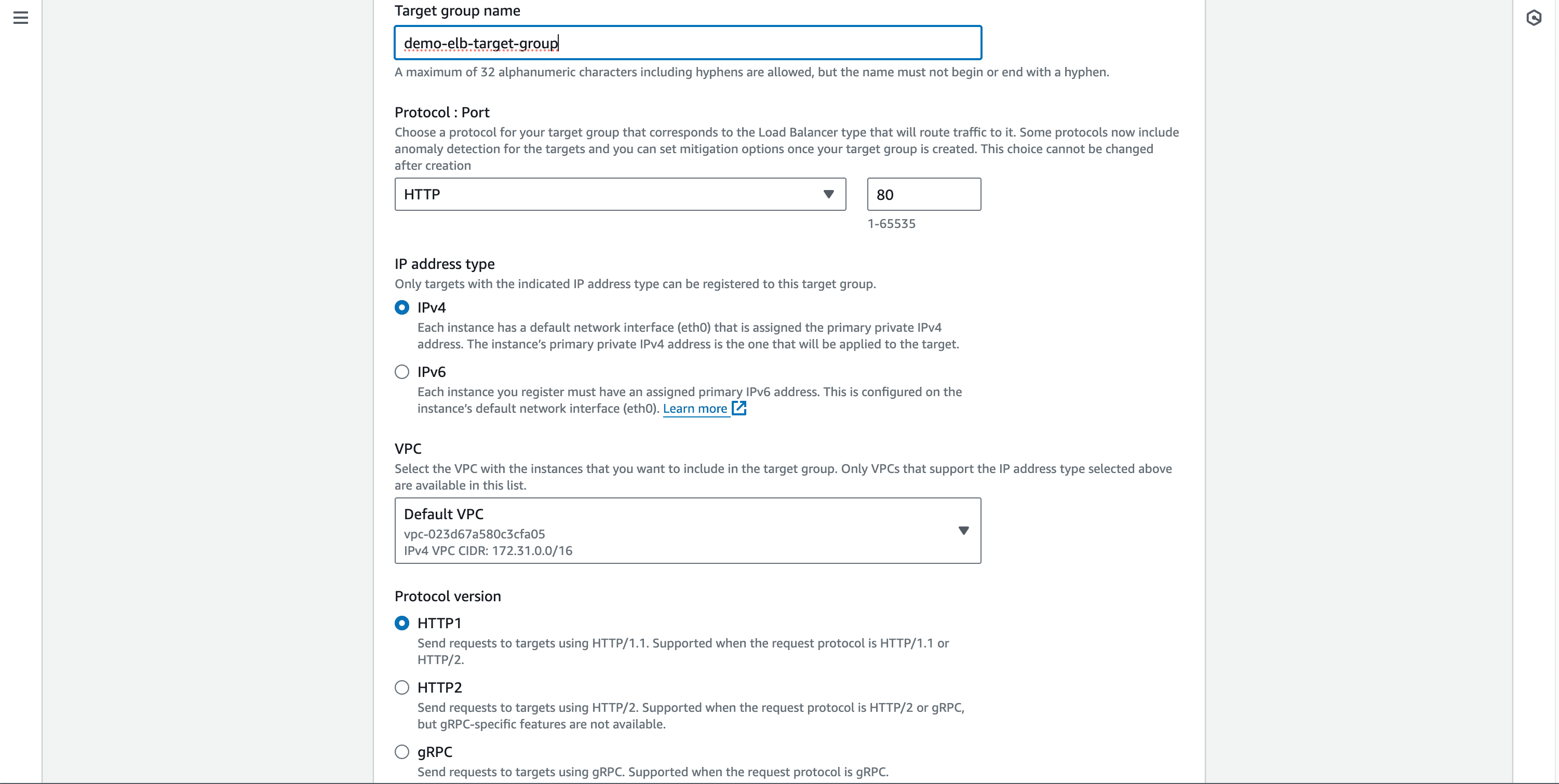
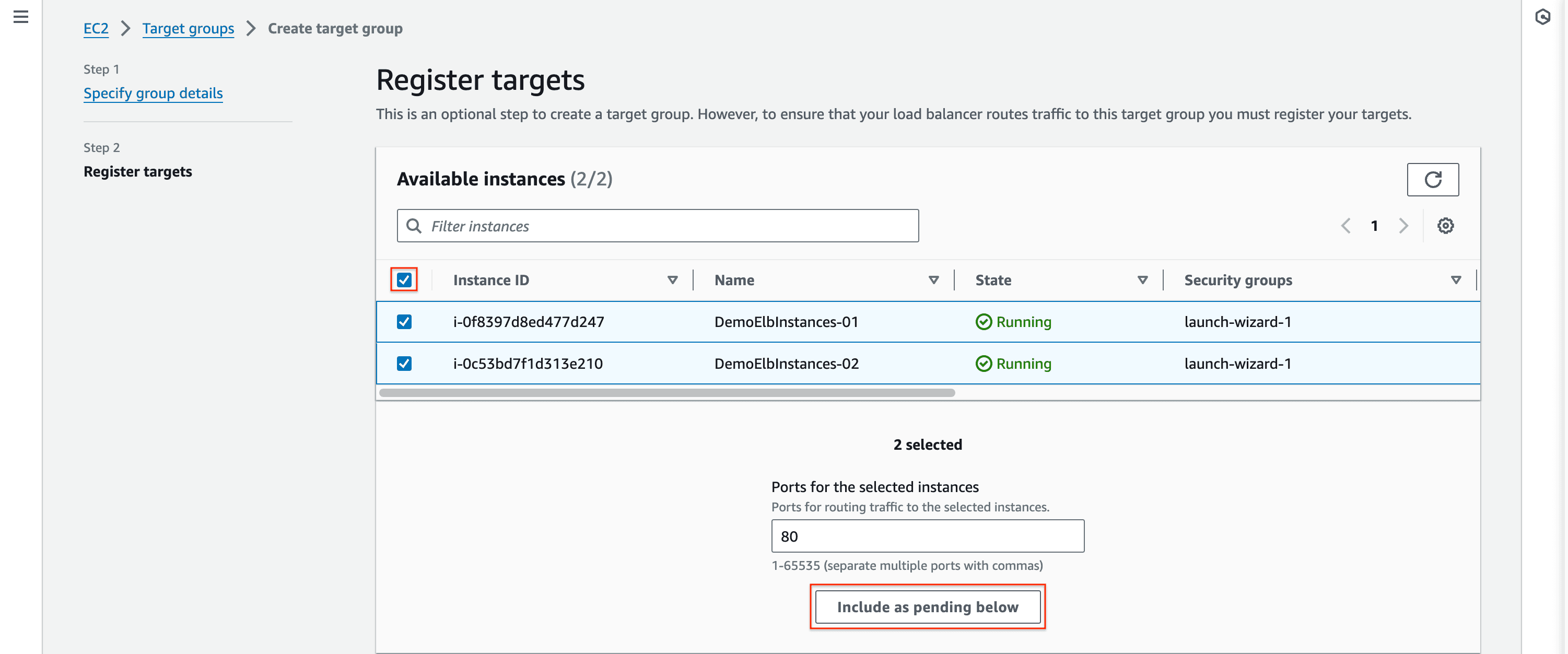
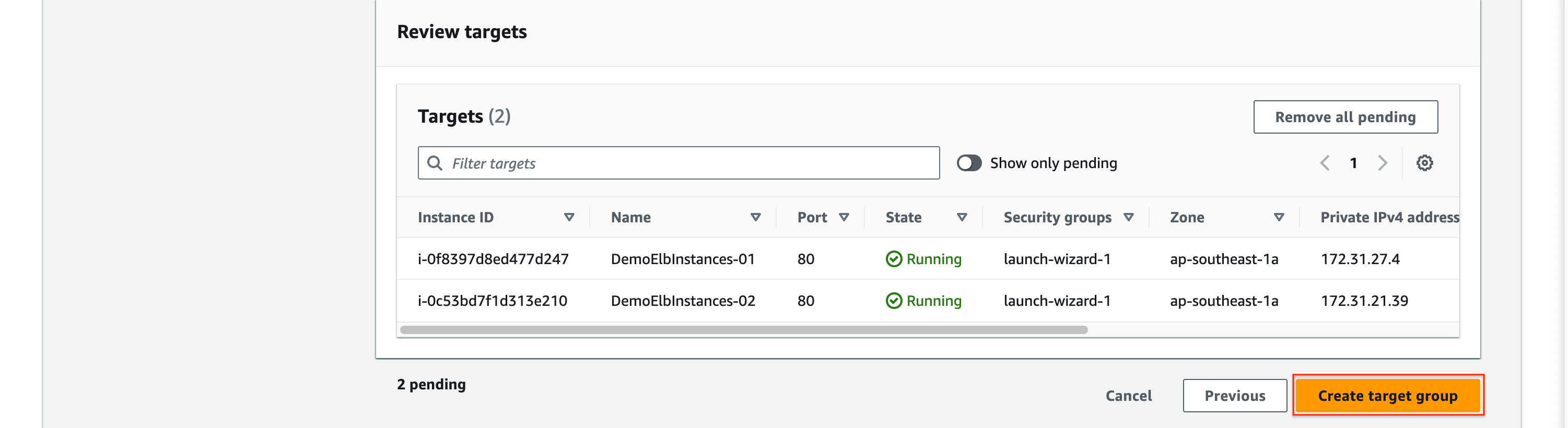
- Leave other options default and click
Create load balancer.
- Wait for
Statusis changed toActiveand Application Load Balancer was created successfully.
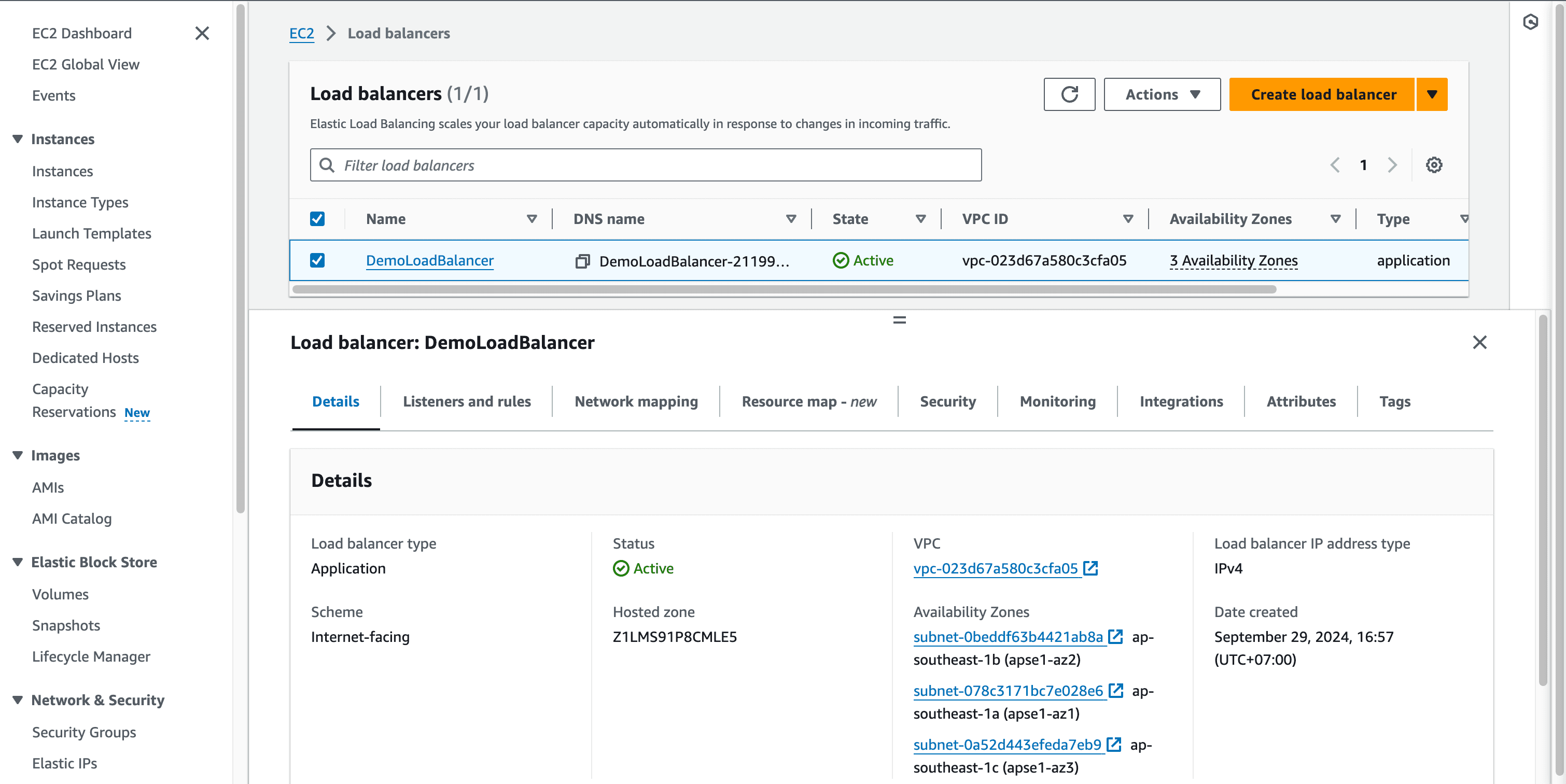
- Copy the
DNS nameand paste it on the browser then you can see the requests auto redirect to one of two created instances.
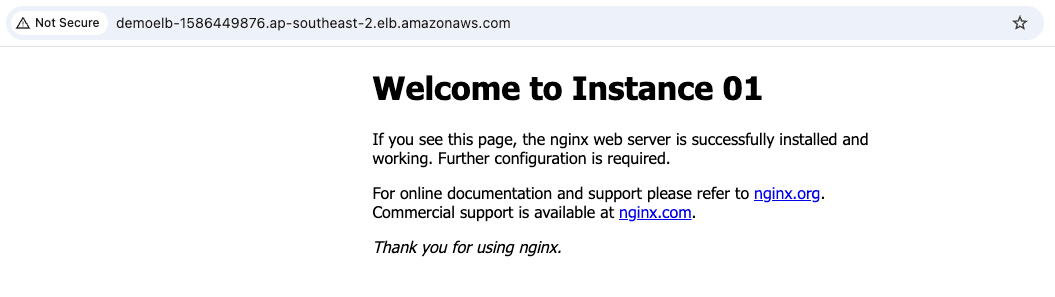
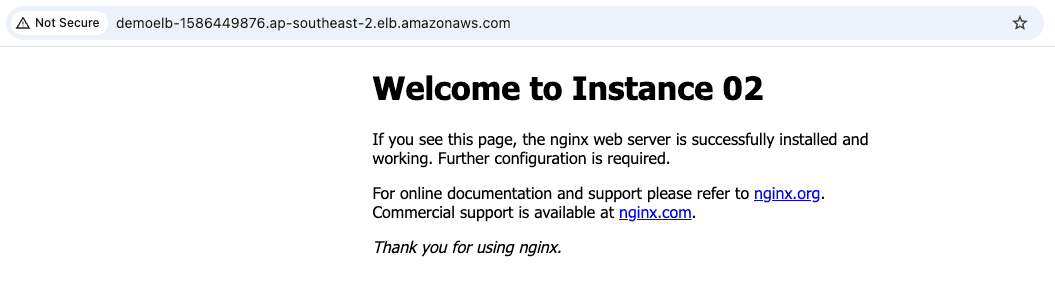
6. Conclusion.
In this post, we covered the basics of AWS Load Balancer, explored its features, and created a demo with Application Load Balancer. I hope this article provides useful insights and helps you better understand Elastic Load Balancer. In the next post, we will discuss about Auto Scaling Group and use it to create a collection of Amazon EC2 instances treated as a logical unit.
See you in the next posts. Happy Coding!